Pipeline
We possess multiple pipelines that leverage the properties of 211At, including af-001(TAH-1005) and af-002(PSW-1025), which are currently being evaluated in clinical trials. Furthermore, we are advancing proof-of-concept studies in the discovery phase for both cell membrane surface and intracellular targets, combining 211At with small molecules and peptide ligands.
af-001(TAH-1005)
target:NIS(Symporter)
Thyroid Cancer (RAl-refractory)
af-001
target:NIS(Symporter)
Thyroid Cancer (RAI-naïve)
af-002(PSW-1025)
target:PSMA(Cell membrane)
Prostate Cancer (Refractory)
af-003
target:LAT1(Transporter)
Pan-Cancer
Tanabe-Veneno
target:Undisclosed
Multiple Molecular Targets
In-house Program
target:Undisclosed
Multiple Molecular Targets
af-001 (TAH-1005)

![甲状腺癌患者における[211At]NaAt投与前後の131I集積画像の経時的変化](/assets/img/illust-pipeline2_2oncB7.webp)
- Waterfall plots showing the maximum change in serum thyroglobulin levels at 3 or 6 months after administration of [211At]NaAt. (* Measured without rhTSH stimulation.)
- Representative 131I planar and SPECT/CT images in a patient with follicular thyroid cancer with multiple bone metastasis at baseline, and at 3 and 6 months after administration of [211At]NaAt (3.5MBq/kg). A gradual decrease in 131I accumulation in the lumbar spine and sacral metastases was observed over time.
Quotation:
Watabe T., Mukai K., Naka S. et al. First-in-Human Study of [211At]NaAt as Targeted α-Therapy in Patients with Radioiodine-Refractory Thyroid
Cancer (Alpha-T1 Trial). Journal of Nuclear Medicine September 2025, DOI:
https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.125.270810
af-002 (PSW-1025)
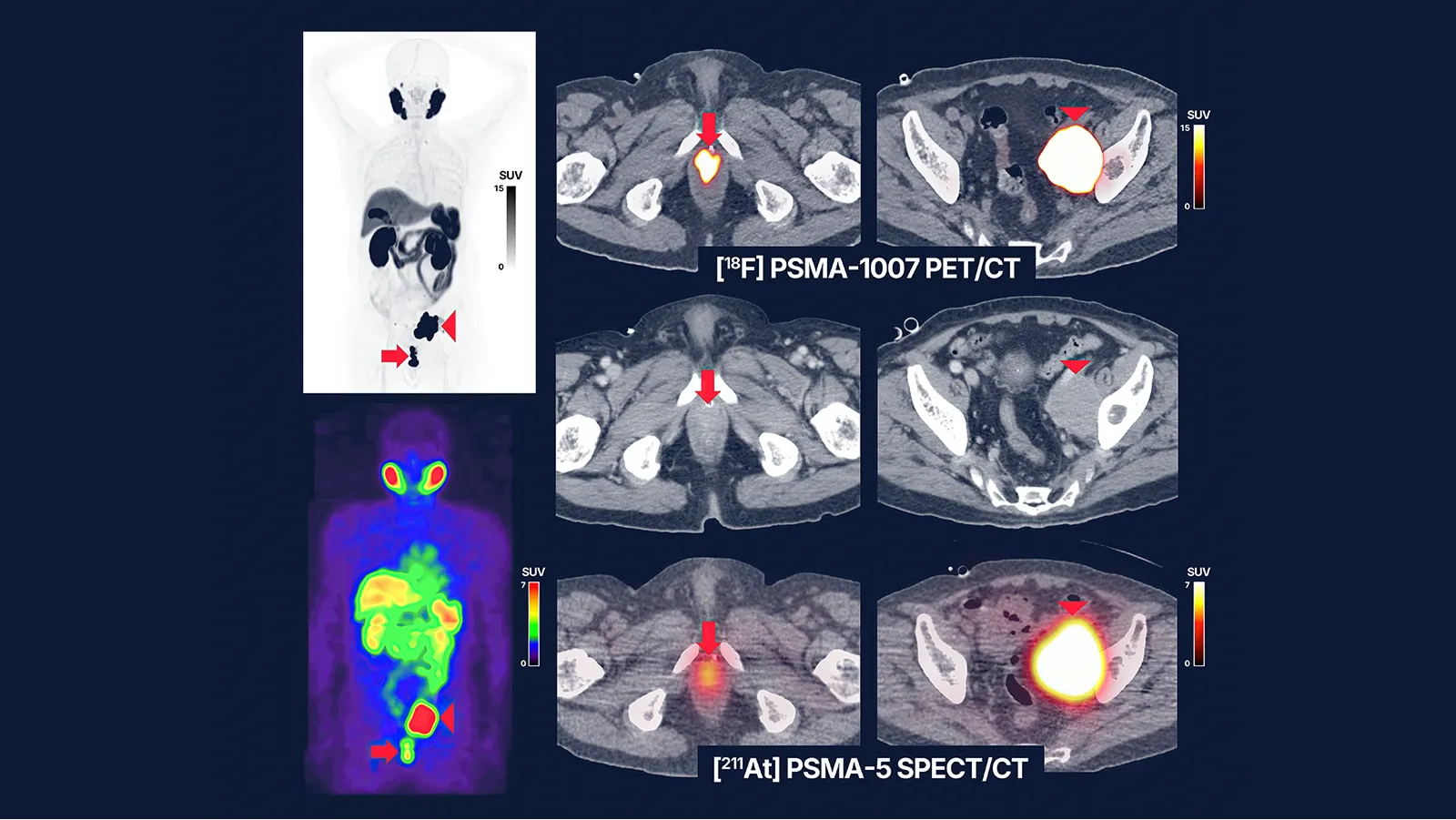
- Pre-treatment [18F]PSMA-1007 PET/CT (A) and [211At]PSMA-5 SPECT/CT (B) images showed similar distribution patterns, with high uptake in recurrent/metastatic lesions (left: maximum intensity projection, right: fusion and contrast-enhanced CT images). Both images revealed high accumulation in the soft tissue mass within the prostate area (SUVmax = 60.7 on [18F]PSMA-1007 PET and 4.9 on [211At]PSMA-5 SPECT) (arrows) and in the enlarged left external iliac lymph node metastasis (SUVmax = 143.7 and 17.6, respectively) (arrow heads). Physiological accumulation was similarly observed in both modalities in the salivary glands, liver, spleen, small intestine, and kidneys, with no detectable urinary excretion. This image provides proof-of-concept for a theranostic approach using the 18F/211At-labeled compound pair.
Quotation:
Watabe, T., Hatano, K., Naka, S. et al. First-in-human SPECT/CT imaging of [211At]PSMA-5: targeted alpha therapy in a patient with refractory prostate
cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 52, 2253–2255 (2025).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-024-07017-w